Using Gitlab, Terraform, and Ansible to spin up a Gitlab Runner hosted on Digital Ocean
As part of my One App Three Ways: Weather work I had to set up a Gitlab Runner that would that would support running the Android Emulator. Specifically, I needed a virtual machine that would support KVM and QEMU. I didn't want to do this set up by hand, so I leveraged Gitlab's CI capability along with Terraform and Ansible to be able automatically spin up and tear-down a runner. I've added my referral link at the bottom of the page. This will get you $100 credit. That's equal to two months of CI hosting.
The work is broken up into three primary pieces The Gitlab CI file that uses a Terraform template to run the deployment and keep track of state The Terraform script that provisions a virtual machine with Digital Ocean * The Ansible script that configures the virtual machine with Docker and the Gitlab Runner, and dependencies for the Android Emulator
The VM size to support running the Android Emulator is one with 8GB of RAM available. These VMs start at about $50 per month. The actual terraform folder structure is the main tf file with a digital ocean module that does the work. I also heavily leverage the CI varables capability in Gitlab to hide secrets.
include:
- template: Terraform.latest.gitlab-ci.yml
stages:
- validate
- test
- build
- deploy
- configure
- cleanup
variables:
TF_IN_AUTOMATION: "true"
TF_STATE_NAME: development
TF_CACHE_KEY: development
TF_ROOT: sources/terraform
TF_VAR_droplet_name: "gitlab-runner"
TF_VAR_droplet_image: "ubuntu-22-04-x64"
TF_VAR_droplet_size: "s-4vcpu-8gb"
TF_VAR_droplet_region: "nyc1"
TF_VAR_ssh_fingerprint: "${FINGERPRINT}"
TF_VAR_do_token: "${DO_TOKEN}"
TF_VAR_pub_key: "${PUBLIC_KEY}"
TF_VAR_pvt_key: "${PRIVATE_KEY}"
TF_LOG: "DEBUG"
SOME_VAR: 0
fmt:
allow_failure: false
validate:
extends: [.terraform:validate]
before_script:
- bin/add-dependencies.sh
- bin/tell-secrets.sh
build:
extends: [.terraform:build]
before_script:
- bin/add-dependencies.sh
- bin/tell-secrets.sh
deploy:
extends: [.terraform:deploy]
before_script:
- bin/add-dependencies.sh
- bin/tell-secrets.sh
script:
- !reference [.terraform:deploy, script]
- gitlab-terraform output -json > output.json
environment:
name: $TF_STATE_NAME
artifacts:
paths:
- ${CI_PROJECT_DIR}/${TF_ROOT}/output.json
configure:
stage: configure
needs: [deploy]
before_script:
- bin/add-dependencies.sh
- bin/tell-secrets.sh
script:
- export DEPLOYMENT_ADDRESS=$(jq -r .infra_ip_address.value ${CI_PROJECT_DIR}/${TF_ROOT}/output.json)
- echo $DEPLOYMENT_ADDRESS >> inventory
- ansible-playbook -u runner -i inventory --private-key "${PRIVATE_KEY}" -e "pub_key=${PUBLIC_KEY}" -e "runner_token=${RUNNER_TOKEN}" sources/ansible/runner-playbook.yml
destroy:
extends: [.terraform:destroy]
needs: []
before_script:
- bin/add-dependencies.sh
- bin/tell-secrets.sh
environment:
name: $TF_STATE_NAME
action: stop
The Digital Ocean Terraform Module
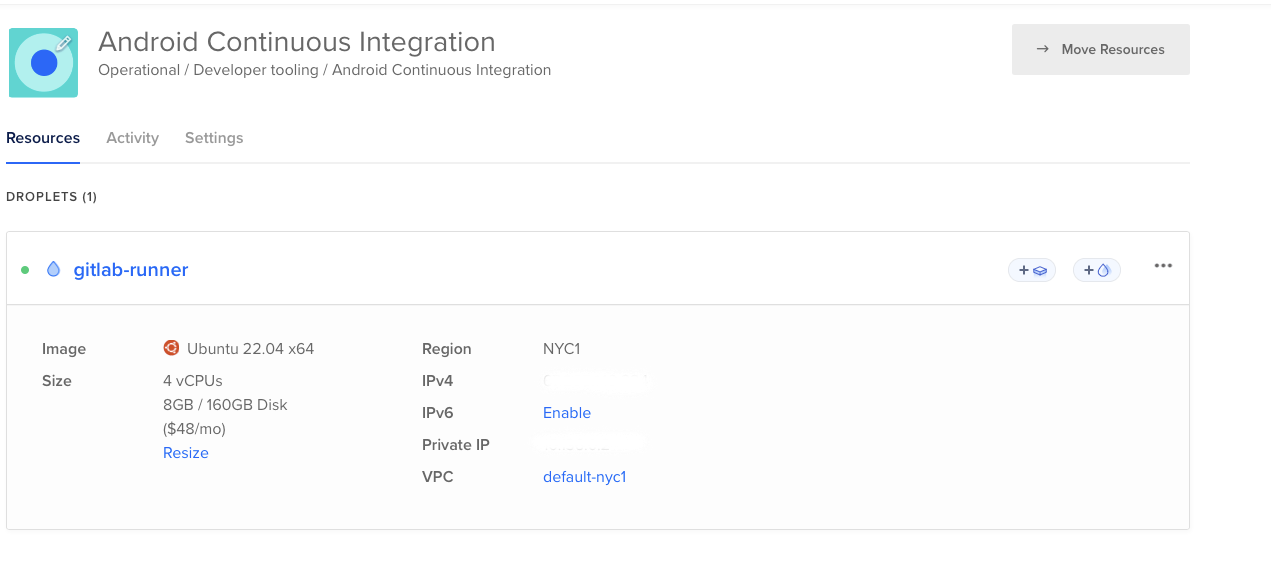
The module uses cloud-config to create a sudoing non-root user for the VM. Once the VM is provisioned, the IP address is stored as an artifact in the Gitlab pipeline to be used by Ansible in configuring the VM.
terraform {
required_providers {
digitalocean = {
source = "digitalocean/digitalocean"
version = ">= 2.21.0"
}
}
}
provider "digitalocean" {
# Provider is configured using environment variables:
# DIGITALOCEAN_TOKEN, DIGITALOCEAN_ACCESS_TOKEN
token = var.do_token
}
data "digitalocean_ssh_key" "terraform" {
name = "gitlab-runner"
}
# Create a new Web Droplet in the nyc2 region
resource "digitalocean_droplet" "runner" {
image = var.droplet_image
name = var.droplet_name
region = var.droplet_region
size = var.droplet_size
monitoring = true
ssh_keys = [
data.digitalocean_ssh_key.terraform.id
]
user_data = file("./runner/runner.yml")
}
You should be able to see the runner in the Digital Ocean Dashboard
[ ]
]
The Ansible playbook
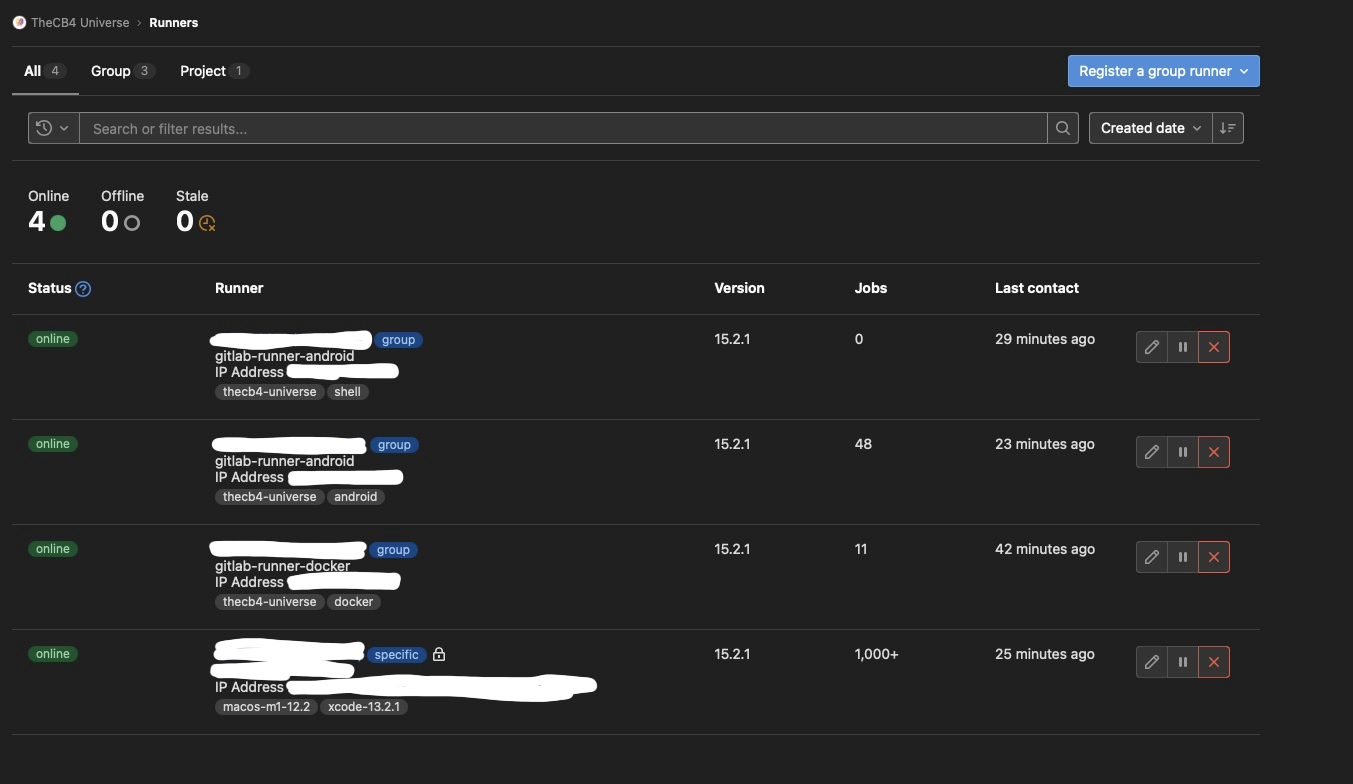
I create different runners. THe first runner runs the plain docker image; this one is used to create the Android Emulator image. The second runner runs the android emulator image. The last runner is a shell runner, for more general purpose CI if needed. Note that both the plain docker and the android images are running in priviledged mode. This is to provide docker access to KVM on the host.
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: gitlab-runner
become: true
tasks:
- name: Gather all facts of cloud init
community.general.cloud_init_data_facts:
register: result
- ansible.builtin.debug:
var: result
- name: Wait for cloud init to finish
community.general.cloud_init_data_facts:
filter: status
register: res
until: "res.cloud_init_data_facts.status.v1.stage is defined and not res.cloud_init_data_facts.status.v1.stage"
retries: 50
delay: 5
- name: Update APT Cache
apt:
update_cache: yes
force_apt_get: yes
- name: Upgrade all packages to the latest version
apt:
name: "*"
state: latest
force_apt_get: yes
- name: install dependencies dependencies
apt:
name: "{{item}}"
state: present
# update_cache: yes
loop:
- apt-transport-https
- ca-certificates
- curl
- gnupg-agent
- software-properties-common
- cpu-checker
- qemu-system-x86
- libvirt-daemon-system
- libvirt-clients
- bridge-utils
- name: add docker GPG key
apt_key:
url: https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg
state: present
- name: add Docker repository to apt
apt_repository:
repo: deb https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bionic stable
state: present
- name: install docker
apt:
name: "{{item}}"
state: latest
# update_cache: yes
loop:
- docker-ce
- docker-ce-cli
- containerd.io
- name: check docker is active
service:
name: docker
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: Ensure group "docker" exists
ansible.builtin.group:
name: docker
state: present
- name: adding runner to docker group
user:
name: gitlab-runner
groups: docker
append: yes
- name: Install docker-compose
get_url:
url: https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-Linux-x86_64
dest: /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
mode: 'u+x,g+x'
- name: Change file ownership, group and permissions
ansible.builtin.file:
path: /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
owner: gitlab-runner
group: docker
- name: install gitlab-runner dependencies
apt:
name: "{{item}}"
state: present
# update_cache: yes
loop:
- apt-transport-https
- name: Install gitlab runner
shell: |
curl -LJO https://gitlab-runner-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/deb/gitlab-runner_amd64.deb
dpkg -i gitlab-runner_amd64.deb
args:
creates: /usr/bin/gitlab-runner
- name: Docker Prune
ansible.builtin.cron:
name: Docker Prune
minute: "15"
job: /usr/bin/docker system prune -f
state: present
user: gitlab-runner
- name: Register gitlab docker runner
command: |
gitlab-runner register \
--non-interactive \
--url "https://gitlab.com/" \
--registration-token "{{ runner_token }}" \
--executor "docker" \
--docker-image docker:latest \
--description "gitlab-runner-docker" \
--tag-list "thecb4-universe, docker" \
--run-untagged="false" \
--locked="true" \
--docker-privileged
- name: Register gitlab android image runner
command: |
gitlab-runner register \
--non-interactive \
--url "https://gitlab.com/" \
--registration-token "{{ runner_token }}" \
--executor "docker" \
--docker-image registry.gitlab.com/thecb4-universe/private/docker/android-x86_64:latest \
--description "gitlab-runner-android" \
--tag-list "thecb4-universe, android" \
--run-untagged="false" \
--locked="true" \
--docker-privileged
- name: Register gitlab shell runner
command: |
gitlab-runner register \
--non-interactive \
--url "https://gitlab.com/" \
--registration-token "{{ runner_token }}" \
--executor "shell" \
--shell "bash"
--description "gitlab-runner-android" \
--tag-list "thecb4-universe, shell" \
--run-untagged="false" \
--locked="true" \
- name: adding runner to libvirt group
user:
name: gitlab-runner
groups: libvirt
append: yes
- name: adding runner to kvm group
user:
name: gitlab-runner
groups: kvm
append: yes
You should be able to see the runners with all greens in your group
[ ]
]
Find me on Twitter and tell me all about it! Digital Ocean referal is here